Bed bugs and ticks are two prevalent pests that are both known to cause discomfort and health issues. While they share some similarities, their behaviors and habitats differ significantly. When comparing bed bug vs tick, it's important to understand their unique characteristics and how they interact with their environments. This article will delve into the key distinctions between these pests, their potential risks, and effective strategies for prevention and control.
Appearance Differences Between Bed Bugs and Ticks
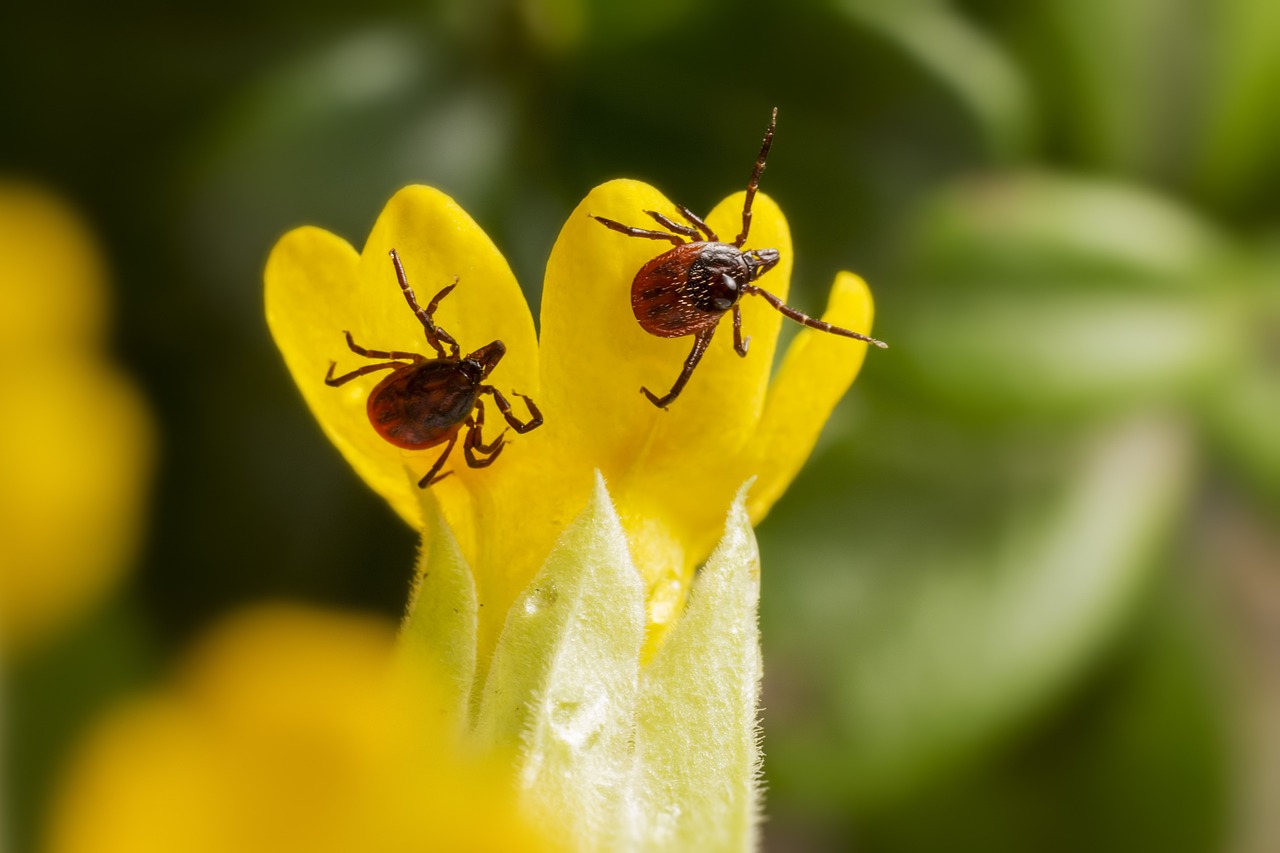
Bed bugs and ticks may appear similar at first glance, but they have distinct physical differences. Bed bugs are flat, oval-shaped insects with a reddish-brown color and six legs. They have a slightly elongated body that expands after feeding on blood. Adult bed bugs are usually around 5-7 millimeters long and lack wings, so they cannot fly. Ticks, on the other hand, are arachnids with eight legs, giving them a spider-like appearance. Their bodies are more rounded and leathery, and they vary in color from brown to reddish-brown or black. One of the most distinguishing facts about ticks is that, unlike bed bugs, they are capable of latching onto their hosts for extended periods, often appearing swollen after feeding. Ticks are generally smaller than bed bugs, though they can vary in size depending on the species and how engorged they are with blood. Recognizing these differences helps distinguish the two pests.
Natural Habitats of Bed Bugs and Ticks
Bed bugs typically thrive in human habitats, favoring areas close to sleeping environments. They are often found in mattresses, box springs, bed frames, and upholstered furniture, where they can easily access their primary food source: human blood. These pests are known for their ability to hide in tiny crevices, making them prevalent in places like hotels, hostels, and apartments, especially where there is a high turnover of occupants. Conversely, ticks live in outdoor environments and are commonly found in wooded or grassy areas. They thrive in humid conditions, often residing in leaf litter, tall grass, and shrubs, where they wait for hosts to pass by. Ticks tend to attach themselves to animals, including pets and wildlife, but they can also latch onto humans.
Signs of Bed Bug and Tick Infestations
Signs of a bed bug infestation often include small, reddish-brown spots on bedding, which are usually blood stains from feeding, as well as dark spots of excrement that resemble tiny ink stains. You might also notice a musty odor in heavily infested areas. Recognizing these signs of bed bug infestation early is crucial for effective management. Bed bugs themselves can be found in seams, folds, and crevices of mattresses and furniture, particularly at night when they are most active.
In contrast, the signs of tick infestation are often indicated by the presence of ticks, which may be found on clothing, skin, or pets after outdoor activities. A telltale sign of a tick bite is the appearance of a small, red bump, often with a darker center, and some may develop a characteristic “bull’s-eye” rash, particularly in the case of Lyme disease. Additionally, the presence of larvae, which look like small black or brown specks, can signal an abundance of ticks in the area.
Distinguishing Bed Bug Bites from Tick Bites
Bed bug bites typically manifest as small, red, itchy welts arranged in a line or cluster on exposed skin. These bites are often referred to as "breakfast, lunch, and dinner" bites, indicating a series of feedings in a single area. These bites can become inflamed and may take several days to heal, with some individuals experiencing allergic reactions that lead to more severe itching and discomfort. Tick bites often present as a small, red bump that may or may not be itchy. The severity of symptoms caused by a tick bite can vary depending on the tick species and whether it carries diseases. A distinguishing feature of certain tick bites is a "bull's-eye" rash, especially in cases of Lyme disease. Both bed bug and tick bites can lead to secondary infections if scratched, but tick bites may also cause systemic symptoms like fever and fatigue due to transmitted pathogens, making them a more serious concern in some cases.
Health Risks and Diseases from Bed Bugs and Ticks
Bed bug bites, while generally not associated with serious health risks, can lead to significant discomfort and distress due to itching and irritation. In some cases, scratching the bites can result in secondary skin infections. Additionally, the psychological impact of a bed bug infestation can lead to anxiety and insomnia, affecting overall well-being. Tick bites pose more severe health risks as they can transmit various diseases. Among the most notable is Lyme disease, characterized by flu-like symptoms and the distinctive "bull's-eye" rash. Other illnesses transmitted by ticks include Rocky Mountain spotted fever, anaplasmosis, and babesiosis, which can lead to complications if not treated promptly. The most common symptoms of tick-borne diseases include fever, chills, aches and pains, and distinctive rashes. These symptoms can range from mild to severe, potentially resulting in long-term health issues if left untreated.

Preventive Measures for Bed Bugs and Ticks
Preventing infestations of bed bugs and ticks involves proactive measures in both indoor and outdoor environments. For bed bugs, it’s essential to conduct regular inspections of mattresses, bedding, and furniture, especially when traveling or acquiring second-hand items. Following certain bedbug guidelines can help ensure thorough searches. Encasements for mattresses and box springs can serve as barriers, making it difficult for bed bugs to hide. Reducing clutter in sleeping areas also minimizes potential hiding spots. For ticks, maintaining a well-manicured yard is crucial. Regularly mowing the lawn, clearing away leaf litter, and creating a buffer zone of gravel or wood chips between your yard and wooded areas can deter ticks. Wearing long sleeves and pants when in grassy or wooded areas, and using insect repellent with DEET can also be effective. Finally, promptly checking for ticks after outdoor activities and showering soon after returning indoors can help catch any that may have latched on, reducing the risk of disease transmission.
Pest Control Solutions for Bed Bugs and Ticks
Effective solutions for bed bug pest control and tick pest control include both professional treatments and DIY methods. When considering bed bug vs tick control, it's essential to recognize that these pests require different approaches. For bed bugs, professional exterminators often employ heat treatments, which raise the temperature in infested areas to lethal levels for the pests. Chemical insecticides may also be used, targeting both adult bugs and their eggs. Additionally, vacuuming infested areas and using encasements on mattresses can aid in management. DIY methods include using diatomaceous earth, a natural powder that disrupts the exoskeleton of insects, or steaming infested items to kill bugs on contact. To get rid of ticks, professional pest control can involve applying acaricides to yard areas where ticks are prevalent. Homeowners can also use DIY strategies such as maintaining a tidy yard, removing potential tick habitats, and wearing permethrin-treated clothing for outdoor activities. Regularly checking pets for ticks and using veterinarian-recommended tick prevention products is crucial to keeping infestations at bay.
Understanding the differences between bed bugs and ticks is essential for effective pest management. Whether you need residential pest control or commercial pest control solutions, Twin-Boro’s team is here to help. For expert assistance in tackling these pests, contact us today to protect your home or business.